Batts, Blown-in and Radiant Barrier, Oh My.
- A. Carter
- Mar 28, 2018
- 2 min read
Updated: Apr 10, 2018
The first step to understanding insulation is understanding R-Value. Simply put, R stands for resistance to heat flow. R-Value is an equation to determine a material's resistance to heat flow based on its’ density.
The higher the R-Value the greater the resistance to heat flow.
Colder climates typically require higher R-Values than more temperate areas.
R-Value is not the be all end all for insulation but it is a good place to start. Depending on where you live and the area you are installing you will want different R-Values. For exterior walls typically anywhere from R-13 to R-23 is sufficient while you will want R-30 to R-49 for ceilings and attic spaces.

Different Types of Insulation: Form
•Loose-fill / blown-in
•Batts and rolls / blanket
•Foam or rigid board
•Reflective
Different Types of Insulation: Materials
•Fiberglass
•Cellulose
•Radiant barrier
•Foam
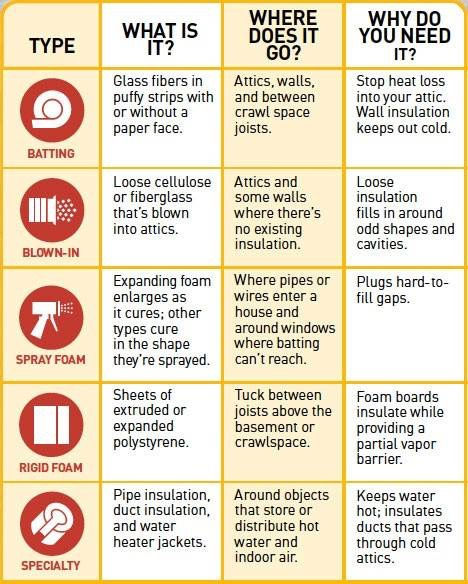
Batt or Roll Insulation

The most common type of insulation is Batt and Roll insulation, also known as blanket insulation. This is the insulation that looks like pink cotton candy. It is made from fiberglass or different fibers and in some cases cotton which is called “blue jean” insulation. You typically see this in floors, ceilings and walls.

This insulation R-Value is measured per inches. We are looking at a 3.0 -4.0 R Value per inch of insulation. Builders will have wall insulation somewhere between R-13 to R-23 for walls.
Fiberglass insulation will usually have some type of facing. Either a Kraft paper or plastic to help control moisture, mold and drafts.
Blown-In Insulation

Loose-fill or blown-in insulation is another of the most common types of insulation and works exactly how it sounds. It is blown into a wall cavity or designated space using special equipment. The most common form of blown-in insulation is cellulose but it can also be made with fiberglass, foam and mineral wool. Builders will sometimes offer this insulation form as an upgrade in attic spaces up to R-38. This is a good option for unfinished attic spaces or oddly shaped spaces or the corners, edges and around framing.
Spray-Foam Insulation
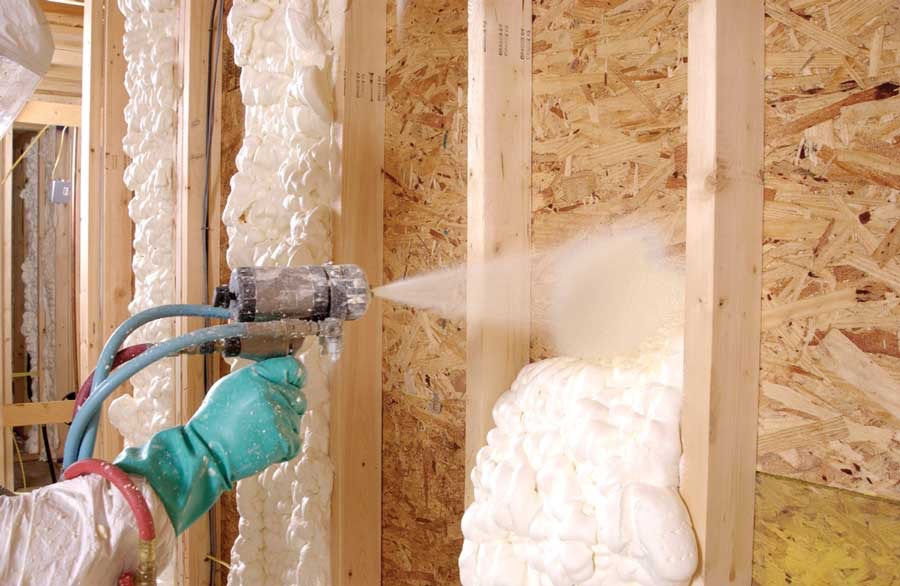

Spray-foam is becoming more and more popular in new construction homes. A bit more difficult to install than Batt or blanket insulation due only for the need for the spray machine that sprays the foam and a small amount of training to work said machine. This type of insulation does create a termal, air and moisture barrier.
Radiant Barrier

Radiant barrier is a form of reflective insulation, typically installed in attic ceilings under the roof. It helps your home reflect heat from the sun.




Comments